In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, ERP software for competitive advantage has emerged as a powerful tool, enabling organizations to streamline operations, optimize decision-making, and drive innovation for sustained success. This transformative technology empowers businesses to gain a strategic edge by leveraging real-time data, automating processes, and fostering collaboration.
ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s core processes, from finance and supply chain management to customer relationship management and human resources. By integrating these functions into a single, unified platform, ERP software eliminates data silos, improves communication, and enhances operational efficiency.
ERP Software Overview
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive business management system that integrates various departments and functions of an organization into a unified platform. Its key components include:
Financial Management
Accounts payable/receivable, general ledger, cash management
Human Resources Management
Payroll, benefits, employee data
Supply Chain Management
Inventory management, purchasing, logistics
Customer Relationship Management
Sales, marketing, customer serviceERP systems provide numerous benefits, including:
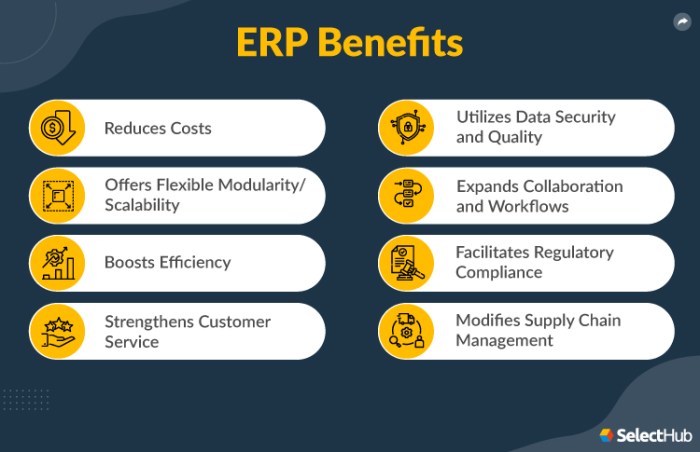
Improved Efficiency
Automates processes, reduces manual labor, and streamlines operations.
Enhanced Data Accuracy
Provides a single source of truth for all business data, eliminating errors and inconsistencies.
Increased Productivity
Frees up employees from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities.
Better Decision-Making
Provides real-time access to data and analytics for informed decision-making.
Improved Collaboration
Facilitates cross-functional collaboration and communication.
Challenges of ERP Implementation
Implementing ERP systems can be challenging due to:
Cost
ERP systems can be expensive to purchase and implement.
Complexity
Integrating different systems and processes can be complex and time-consuming.
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist changes to their established workflows.
Data Migration
Transferring existing data to the new system can be complex and error-prone.
Training
Training employees on the new system can be time-consuming and expensive.
Competitive Advantage through ERP

ERP systems provide organizations with a comprehensive suite of integrated applications that streamline business processes and improve operational efficiency. By consolidating data and automating tasks, ERP systems can significantly reduce costs, improve productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Operational Efficiency
- Centralized data management eliminates data duplication and inconsistencies, improving data accuracy and accessibility.
- Automated workflows streamline processes, reduce manual labor, and improve task execution.
- Real-time visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) enables timely decision-making and proactive problem-solving.
Decision-Making and Planning
- ERP systems provide comprehensive data analysis capabilities that support informed decision-making.
- Scenario planning and simulation tools enable organizations to evaluate different strategies and make data-driven choices.
- Integration with forecasting tools enhances demand planning and supply chain management.
Innovation and Growth
- ERP systems provide a platform for data sharing and collaboration, fostering innovation and knowledge transfer.
- Real-time insights into customer behavior and market trends support product and service development.
- Streamlined operations and improved efficiency free up resources for research and development.
ERP Software Evaluation
ERP software evaluation is a critical process that helps organizations select the right solution for their specific needs. It involves assessing various factors, including functionality, scalability, cost, and vendor support. By carefully evaluating ERP software solutions, organizations can gain a competitive advantage by streamlining operations, improving efficiency, and enhancing decision-making.
Key Criteria for ERP Software Selection
When selecting an ERP system, it is essential to consider the following key criteria:
- Functionality:The ERP system should align with the organization’s business processes and provide the necessary modules and features to support its operations.
- Scalability:The system should be able to adapt to the organization’s growth and changing business needs.
- Cost:The total cost of ownership, including software licensing, implementation, maintenance, and support, should be within the organization’s budget.
- Vendor Support:The vendor should provide reliable support, including technical assistance, training, and upgrades, to ensure the system’s smooth operation.
- Implementation:The implementation process should be well-managed to minimize disruption and ensure a successful rollout.
Importance of Vendor Selection and Implementation Support
Vendor selection is crucial for the success of an ERP implementation. Organizations should carefully evaluate the vendor’s reputation, experience, and financial stability. They should also consider the vendor’s commitment to ongoing support and upgrades.Implementation support is equally important. A skilled implementation team can help organizations customize the ERP system to meet their specific needs, train users, and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
ERP Implementation Best Practices
ERP implementation requires meticulous planning and execution to ensure successful outcomes. Here are some best practices to consider:
Early Planning and Communication:Initiate the implementation process with a comprehensive plan that Artikels the project scope, timelines, and resource allocation. Effective communication throughout the project is crucial, keeping stakeholders informed and engaged.
Stakeholder Involvement
Actively involve key stakeholders, including end-users, business leaders, and IT personnel, throughout the implementation. Their input and buy-in are essential for ensuring the ERP system aligns with business objectives and user needs.
Phased Approach
Implement the ERP system in phases to minimize disruption and allow for gradual adoption. This approach enables businesses to test and refine the system in smaller increments, reducing the risk of major setbacks.
Change Management
ERP implementation inevitably involves significant organizational change. Effective change management strategies, such as training, communication, and support, are crucial for mitigating resistance and ensuring user acceptance.
Data Migration
Plan and execute data migration meticulously to ensure data integrity and accuracy. This includes data cleansing, mapping, and testing to minimize errors and maintain data quality.
Vendor Support
Establish a strong partnership with the ERP vendor to access technical expertise, training, and ongoing support. This partnership ensures smooth implementation and long-term system maintenance.
Case Studies and Success Stories: ERP Software For Competitive Advantage

Organizations worldwide have leveraged ERP systems to gain significant competitive advantages. Real-world case studies showcase tangible benefits realized by companies that have successfully implemented ERP solutions.
These success stories provide valuable insights into the key factors that contribute to ERP implementation success, enabling organizations to learn from the experiences of others and optimize their own ERP initiatives.
Manufacturing Industry
- Company:XYZ Manufacturing
- Industry:Automotive
- Benefits:
- Reduced production costs by 15%
- Improved inventory management, resulting in a 20% reduction in inventory levels
- Enhanced supply chain visibility, leading to a 10% increase in customer satisfaction
- Key Factors:
- Clear implementation plan with defined goals and objectives
- Strong leadership and stakeholder buy-in
- Comprehensive training and change management program
Retail Industry
- Company:ABC Retail
- Industry:Fashion
- Benefits:
- Increased sales by 10% through improved customer experience
- Reduced operating costs by 12% due to streamlined operations
- Enhanced data analytics capabilities, enabling better decision-making
- Key Factors:
- Focus on customer-centricity throughout the implementation process
- Investment in robust data integration and analytics tools
- Agile implementation approach that allowed for flexibility and adaptability
Healthcare Industry
- Company:XYZ Hospital
- Industry:Healthcare
- Benefits:
- Improved patient care by providing real-time access to medical records
- Reduced administrative costs by 15% through automation of processes
- Enhanced collaboration among healthcare professionals, leading to better patient outcomes
- Key Factors:
- Strong partnership with the ERP vendor for ongoing support and expertise
- Phased implementation approach to minimize disruption to daily operations
- Emphasis on data security and compliance
Industry-Specific ERP Considerations
ERP systems offer industry-specific solutions that address unique challenges and meet the specific requirements of various industries. These solutions are tailored to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and provide a competitive advantage.
Challenges Addressed by ERP Systems
ERP systems address industry-specific challenges by providing integrated solutions that:
- Improve operational efficiency by automating processes and eliminating manual tasks.
- Enhance data accuracy and integrity, ensuring consistent and reliable information across the organization.
- Facilitate better decision-making by providing real-time visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) and analytics.
- Improve customer service by providing a centralized platform for managing customer interactions and tracking order status.
- Enhance compliance with industry regulations and standards, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
Unique Requirements of Different Industries
Different industries have unique requirements for ERP solutions. For example:
Manufacturing
ERP systems for manufacturing focus on production planning, inventory management, and quality control.
Retail
ERP systems for retail focus on supply chain management, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Healthcare
ERP systems for healthcare focus on patient records management, medical billing, and regulatory compliance.
Financial services
ERP systems for financial services focus on risk management, compliance, and financial reporting.
Examples of Industry-Specific ERP Implementations
Numerous successful ERP implementations have been tailored to specific industries:
Manufacturing
Ford Motor Company implemented an ERP system to streamline production processes, reduce costs, and improve quality control.
Retail
Walmart implemented an ERP system to manage its complex supply chain, improve inventory management, and enhance customer service.
Healthcare
Kaiser Permanente implemented an ERP system to improve patient care, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
Financial services
Citigroup implemented an ERP system to manage risk, comply with regulations, and improve financial reporting.By addressing industry-specific challenges and meeting unique requirements, ERP systems provide a competitive advantage to organizations in various industries.
Future Trends in ERP
ERP technology is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. These trends are driven by the need for businesses to become more efficient, agile, and competitive.Cloud-based ERP, AI, and automation are three of the most important trends shaping the future of ERP.
Cloud-based ERP offers businesses a number of benefits, including reduced costs, increased flexibility, and improved scalability. AI can help businesses to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and gain insights into their data. Automation can help businesses to streamline processes, reduce errors, and improve productivity.These trends are having a significant impact on the way businesses use ERP.
In the future, ERP will become even more essential for businesses that want to stay competitive.
Cloud-based ERP
Cloud-based ERP is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) solution that is hosted in the cloud. This means that businesses do not need to purchase and maintain their own hardware and software. Cloud-based ERP is typically more affordable than on-premise ERP, and it can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
AI in ERP
AI is being used in ERP to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and gain insights into data. For example, AI can be used to:* Automate tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer service.
- Improve decision-making by providing businesses with insights into their data.
- Gain insights into data by identifying trends and patterns.
Automation in ERP
Automation is being used in ERP to streamline processes, reduce errors, and improve productivity. For example, automation can be used to:* Streamline processes by automating tasks such as order processing and inventory management.
- Reduce errors by eliminating human error from processes.
- Improve productivity by freeing up employees to focus on more value-added tasks.
ERP Software Vendors

The ERP software market is dominated by a handful of leading vendors, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These vendors include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, and NetSuite.
SAP is the largest ERP vendor in the world, with a market share of over 25%. SAP’s ERP solutions are known for their scalability, reliability, and deep functionality. However, SAP’s solutions can be expensive and complex to implement.
Oracle is the second largest ERP vendor in the world, with a market share of around 20%. Oracle’s ERP solutions are known for their performance, flexibility, and support for a wide range of industries. However, Oracle’s solutions can also be expensive and complex to implement.
Microsoft is the third largest ERP vendor in the world, with a market share of around 15%. Microsoft’s ERP solutions are known for their ease of use, integration with other Microsoft products, and affordability. However, Microsoft’s solutions may not be as feature-rich as those from SAP and Oracle.
Infor is the fourth largest ERP vendor in the world, with a market share of around 10%. Infor’s ERP solutions are known for their industry-specific functionality, flexibility, and affordability. However, Infor’s solutions may not be as well-known as those from SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft.
NetSuite is the fifth largest ERP vendor in the world, with a market share of around 5%. NetSuite’s ERP solutions are known for their cloud-based delivery, scalability, and ease of use. However, NetSuite’s solutions may not be as feature-rich as those from SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, and Infor.
ERP Software Pricing

ERP software pricing is a complex topic influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors and different pricing models is crucial for organizations to optimize their ERP investment.
Factors influencing ERP software pricing include the number of users, the complexity of the software, the level of customization required, the industry, and the vendor’s reputation.
Pricing Models
Common pricing models for ERP software include:
- Per-user pricing:A fixed cost per user per month or year. Simple to manage, but can be expensive for organizations with a large number of users.
- Concurrent user pricing:A fixed cost for a specified number of concurrent users. More flexible than per-user pricing, but may require organizations to purchase additional licenses during peak usage.
- Subscription pricing:A monthly or annual subscription fee that includes software updates and support. Provides flexibility and predictable costs, but may not be suitable for organizations with fluctuating usage.
- Tiered pricing:Pricing based on the number of modules or features included in the software package. Allows organizations to customize their ERP solution and pay only for the functionality they need.
Tips for Optimizing Costs
- Negotiate with vendors:Explore discounts, payment terms, and bundled pricing options.
- Consider open-source ERP solutions:Open-source ERP software is typically less expensive than proprietary solutions, but may require additional customization and support costs.
- Implement a phased approach:Implement ERP modules gradually, starting with the most critical ones. This can spread out the cost and reduce the risk of overspending.
- Outsource ERP implementation and support:Outsourcing to a managed service provider can reduce internal costs and provide access to specialized expertise.
ERP Software Implementation Timeline
ERP software implementation is a complex and time-consuming process that typically takes several months to complete. The timeline can vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization, the number of modules being implemented, and the availability of resources.
The following are the key milestones and deliverables throughout the ERP implementation process:
Planning and Preparation
- Define project scope and objectives
- Assemble implementation team
- Develop implementation plan
- Select and purchase ERP software
Design and Configuration
- Configure ERP software to meet business requirements
- Develop data conversion plan
- Create user training materials
Testing and Validation
- Test ERP software to ensure it meets requirements
- Validate data conversion
- Train users on new system
Deployment and Go-Live, ERP software for competitive advantage
- Deploy ERP software to production environment
- Monitor system performance and resolve issues
- Provide ongoing support to users
The following factors can impact the ERP implementation timeline:
- Size and complexity of the organization
- Number of modules being implemented
- Availability of resources
- Experience of the implementation team
- Quality of the data being converted
Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP software for competitive advantage is not just a technology investment but a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in the modern market. By harnessing the power of ERP, organizations can gain a competitive edge, drive growth, and achieve long-term success.
FAQ Overview
What are the key benefits of ERP software?
ERP software offers numerous benefits, including improved operational efficiency, enhanced decision-making, increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
How can ERP software help businesses gain a competitive advantage?
ERP systems provide businesses with a real-time view of their operations, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, streamline processes, and respond quickly to market changes.
What are the common challenges associated with ERP implementation?
ERP implementation can be complex and time-consuming, and businesses may face challenges such as data migration, user adoption, and integration with legacy systems.